Dermatology services help people take care of their skin, hair, and nails. These doctors treat many problems, from acne to skin cancer.
A good dermatologist can check for signs of skin issues and provide treatments to keep your skin healthy.

Many people visit dermatologists for common skin concerns. Some go for regular skin checks, while others seek help for specific problems.
Dermatologists offer a wide range of services to meet different needs.
Dermatology clinics often use special tools and methods to look at skin closely. They can do tests to find out what’s causing a rash or other skin issue.
Some clinics also offer cosmetic treatments to improve how skin looks.
Exploring Dermatology Services

Dermatology covers a wide range of medical services focused on skin health and appearance. It encompasses various specialties to address different skin conditions and patient needs.
What is Dermatology?
Dermatology is the medical field that deals with the skin, hair, nails, and related diseases. Dermatologists are doctors who specialize in diagnosing and treating over 3,000 different skin conditions.
They work with patients of all ages, from newborns to the elderly.
These specialists undergo extensive training to handle both common and rare skin issues. Dermatologists use various tools and techniques to examine skin, hair, and nails.
They may perform skin biopsies, prescribe medications, or recommend lifestyle changes.
Dermatology also includes cosmetic treatments to improve skin appearance. Some dermatologists focus on specific areas like skin cancer detection or aesthetic procedures.
Types of Dermatology
Dermatology has several branches to address different aspects of skin health:
- General Dermatology: Deals with common skin conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
- Medical Dermatology: Focuses on treating skin diseases and disorders.
- Cosmetic Dermatology: Offers treatments to enhance skin appearance, such as Botox and laser therapy.
- Pediatric Dermatology: Specializes in skin conditions affecting children and teenagers.
- Surgical Dermatology: Involves procedures like mole removal and skin cancer surgery.
Each type of dermatology subspecialty requires specific skills and knowledge. Some dermatologists specialize in one area, while others practice across multiple fields. Dermatology clinics often offer a range of services to meet diverse patient needs.
Skin Conditions and Diagnoses
Dermatologists treat a wide range of skin conditions using various diagnostic techniques. They work to identify and manage common issues like acne and eczema, as well as more complex disorders.
Common Dermatologic Conditions
Acne is a prevalent skin issue that affects many people. It causes pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads on the face, chest, and back.
Eczema leads to dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It often appears in patches on the arms and behind the knees.
Psoriasis creates scaly, red patches on the skin. These patches can be painful and itchy.
Rosacea causes facial redness and visible blood vessels. It may also produce small, red bumps filled with pus.
Dermatitis is a general term for skin irritation. It can result in a red, itchy rash.
Hives are raised, itchy welts that can appear suddenly on the skin. They often result from allergic reactions.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Dermatologists use various methods to diagnose skin conditions. These include:
- Visual examination
- Dermoscopy
- Skin biopsies
- Patch testing
Dermoscopy uses a special magnifying tool to examine skin lesions in detail. This helps identify potential skin cancers.
Skin biopsies involve taking a small sample of skin for lab analysis. This can confirm diagnoses of certain skin disorders.
Patch testing helps identify allergens causing contact dermatitis. It involves applying small amounts of substances to the skin and observing reactions.
Blood tests may also be used to diagnose systemic conditions affecting the skin.
Skin Cancer and Mohs Surgery
Skin cancer is a serious condition that requires prompt treatment.
Mohs surgery is a specialized and highly effective method for removing certain types of skin cancer while preserving healthy tissue. In simple terms, a doctor removes the cancerous skin layer by layer. After removing each thin layer, they examine it under a microscope to check for cancer cells. This process repeats until no more cancer cells are found. The goal is to eliminate all cancer while preserving as much healthy skin as possible.
Skin Cancer Explained
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer. It occurs when skin cells grow abnormally. The three main types are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas are the most common. They rarely spread to other parts of the body. Melanoma is less common but more dangerous.
Skin Cancer Statistics
Global Incidence
- Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there are between 2 to 3 million cases of non-melanoma skin cancers (primarily basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma) diagnosed worldwide each year.
- Melanoma: Approximately 132,000 cases of melanoma are reported globally each year.
United States Statistics:
- Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer:
- The American Cancer Society estimates that about 5.4 million basal and squamous cell skin cancers are diagnosed annually in the U.S., affecting about 3.3 million people (some individuals have multiple cases).
- Exact numbers are difficult to determine because these cancers are not required to be reported to cancer registries.
- Melanoma:
- An estimated 97,610 new cases of melanoma are expected to be diagnosed in 2023.
- Melanoma accounts for about 1% of skin cancer cases but causes a majority of skin cancer deaths.
- Approximately 7,990 deaths from melanoma are anticipated in 2023.
Prevalence and Risk:
- Lifetime Risk:
- One in five Americans will develop skin cancer by the age of 70.
- Having more than five sunburns doubles your risk for melanoma.
- Age and Gender:
- Melanoma is one of the most common cancers in young adults, especially young women under 30.
- Risk increases with age, but skin cancer can affect people of all ages.
Survival Rates:
- Early Detection:
- The 5-year survival rate for melanoma when detected early is about 99%.
- Survival rates drop significantly if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or other organs.
Regular skin cancer screenings are important for early detection. Doctors look for changes in moles or new growths on the skin.
Risk factors for skin cancer include:
- Sun exposure
- Fair skin
- Family history
- Weakened immune system
Early treatment is key to preventing skin cancer from spreading or becoming more serious.
Mohs Micrographic Surgery Overview
Mohs surgery is a precise technique for removing skin cancer. It has a cure rate of up to 99% for certain types of skin cancer.
During the procedure, the surgeon removes thin layers of skin one at a time. Each layer is examined under a microscope for cancer cells. This process continues until no cancer cells remain.
Mohs surgery offers several benefits:
- Preserves healthy tissue
- Minimizes scarring
- Highly effective for treating basal and squamous cell carcinomas
- Can be used on sensitive areas like the face
Recovery time is typically short. Most patients can return to normal activities within a few days.
Cosmetic Dermatological Procedures
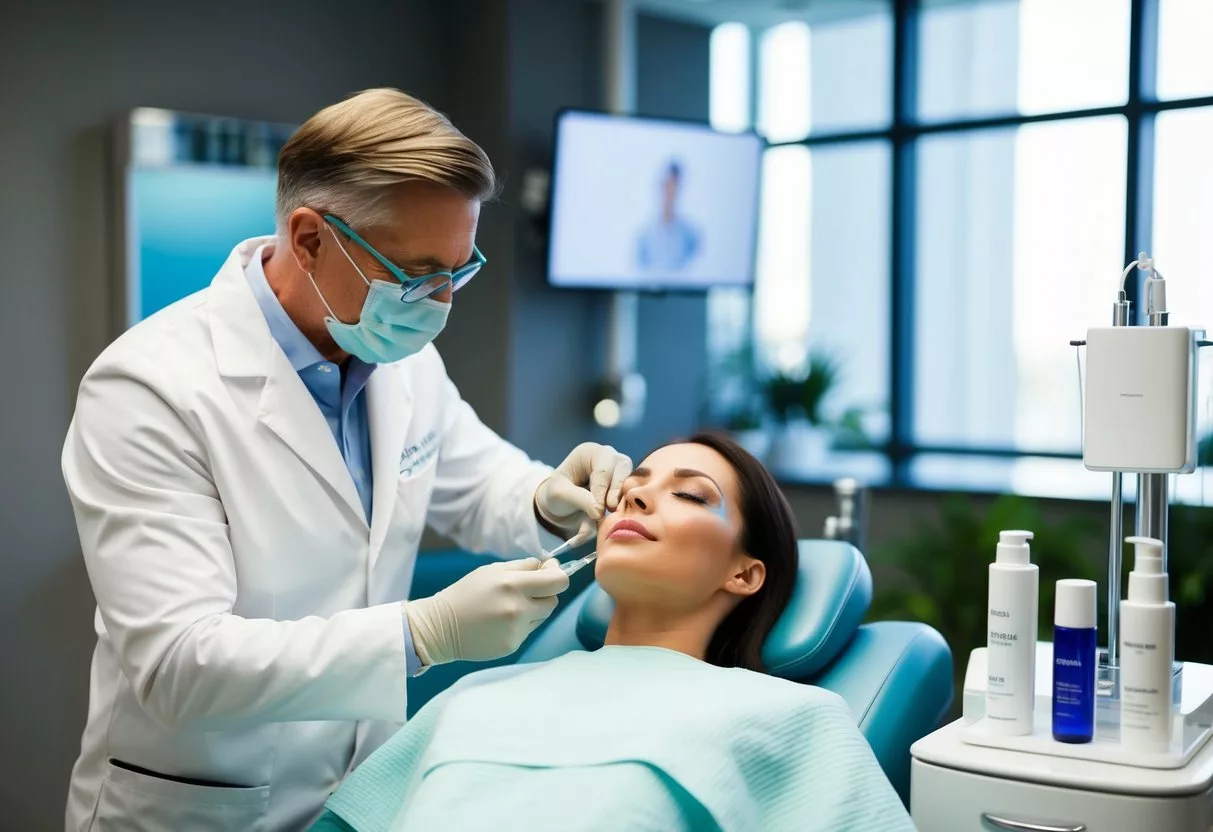

Cosmetic dermatology offers a wide range of treatments to enhance appearance and address skin concerns. These procedures can improve skin texture, reduce signs of aging, and boost self-confidence.
Injectables and Fillers
Injectables and fillers are popular options for treating wrinkles and adding volume to the face.
Botox is a well-known injectable that temporarily relaxes muscles to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. It’s often used for forehead lines, crow’s feet, and frown lines.
Dermal fillers like Restylane can plump up areas of the face that have lost volume due to aging. These fillers are commonly used for:
- Lip enhancement
- Cheek augmentation
- Smoothing nasolabial folds
The effects of fillers typically last several months to a year, depending on the product used and the area treated. These procedures are quick, with minimal downtime, making them attractive options for many patients.
Laser and Light-based Therapies
Laser treatments can address various skin concerns, from age spots to uneven texture. Different types of lasers target specific issues:
- Fractionated lasers for skin resurfacing
- PicoSure for sun damage and uneven tone
- IPL (Intense Pulsed Light) for redness and brown spots
Laser hair removal is another popular treatment that can provide long-lasting results. It works by targeting hair follicles to reduce hair growth over time.
These treatments may require multiple sessions for optimal results. Patients often experience some redness and peeling after laser procedures, but downtime is usually minimal.
Plastic Surgery and Aesthetics
For more dramatic changes, cosmetic surgery offers long-lasting solutions. Common procedures include:
- Facelifts to tighten sagging skin
- Eyelid surgery to reduce under-eye bags
- Rhinoplasty to reshape the nose
Body contouring procedures like liposuction can remove stubborn fat deposits. These surgeries typically require more downtime than non-invasive treatments.
Non-surgical options like CoolSculpting use controlled cooling to eliminate fat cells. This procedure is popular for its minimal downtime and natural-looking results.
Choosing the right procedure depends on individual goals, budget, and willingness to undergo surgery. A consultation with a board-certified dermatologist or plastic surgeon can help determine the best approach.
Pediatric Dermatologic Care
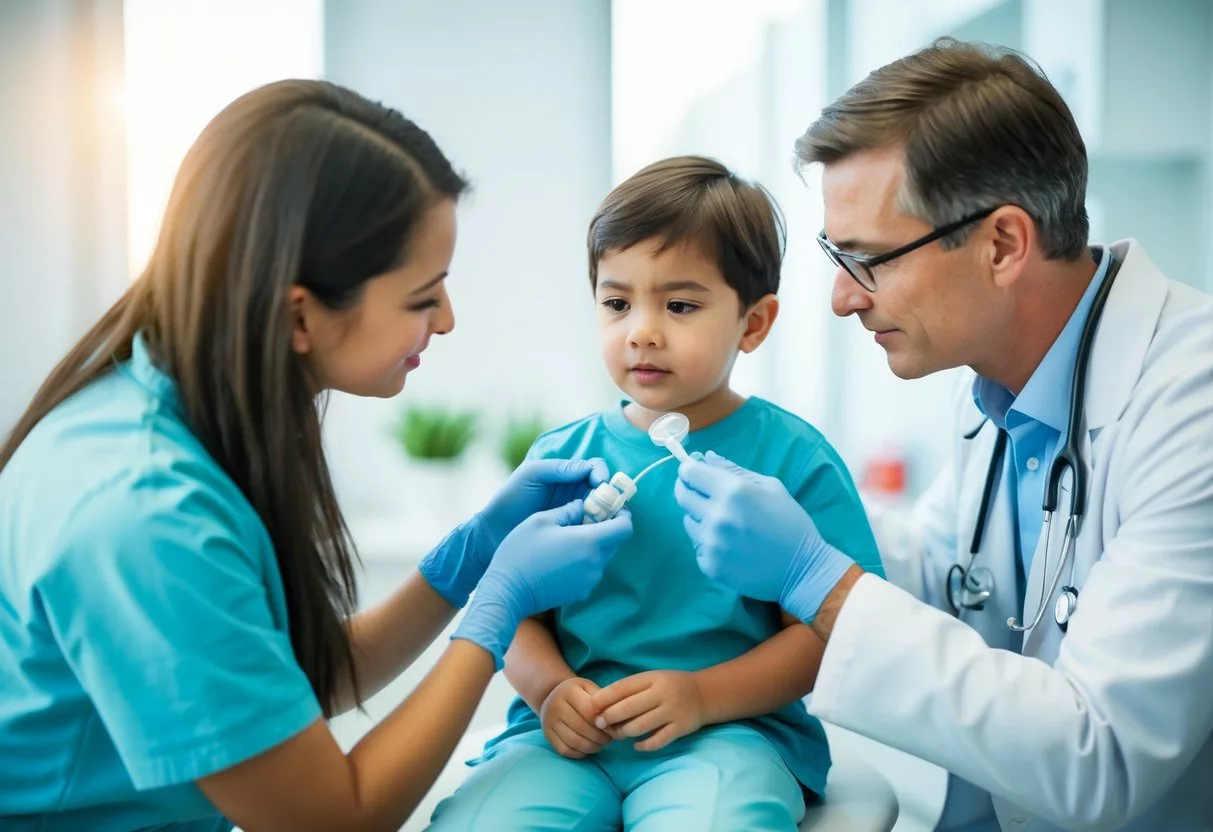

Pediatric dermatology focuses on treating skin conditions in children. It combines knowledge from dermatology, genetics, immunology, and pediatrics to provide specialized care for young patients.
Unique Dermatological Needs of Children
Children’s skin differs from adults in many ways. It’s more sensitive and prone to certain conditions. Pediatric dermatologists have special training to handle these unique needs.
Common issues include:
- Birthmarks
- Eczema
- Acne
- Allergic reactions
- Genetic skin disorders
Pediatric dermatologists use gentle treatments suited for children’s delicate skin. They also consider how skin conditions may affect a child’s growth and development.
Some skin problems in kids have genetic roots. Doctors may use genetic testing to diagnose rare conditions. They work with other specialists to provide complete care.
Birthmarks are a key focus in pediatric dermatology. Some fade on their own, while others may need treatment. Doctors can advise parents on the best approach for each type of birthmark.
Pediatric dermatology experts also deal with immune-related skin issues in children. They use their knowledge of immunology to treat conditions like atopic dermatitis.
Dermatological Therapies

Dermatologists use a range of treatments to address skin conditions. These include topical and oral medications, as well as newer biologic therapies. Each approach targets specific skin issues in different ways.
Topical and Systemic Treatments
Topical treatments are applied directly to the skin. They include creams, ointments, and gels. These often contain steroids, retinoids, or antibiotics. Doctors prescribe them for issues like acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
Systemic treatments work throughout the body. Pills and injections fall into this category. Oral antibiotics can help with severe acne. Antifungal medications treat ringworm and other fungal infections.
Some treatments combine topical and systemic approaches. For example, photodynamic therapy uses light-sensitive drugs and light exposure. This treats certain skin cancers and acne.
Biologic Drugs and New Approaches
Biologic drugs are a newer class of treatments. They target specific parts of the immune system. These drugs help with severe psoriasis, eczema, and other inflammatory skin conditions.
Doctors give biologics as injections or infusions. They work by blocking specific proteins that cause inflammation. This leads to clearer skin for many patients.
New approaches in dermatology include laser therapies and light treatments. These can improve acne scars, remove unwanted hair, and reduce signs of aging. Some lasers target blood vessels to treat rosacea and port-wine stains.
Gene therapy is an emerging field in dermatology. It aims to correct genetic skin disorders. While still experimental, it shows promise for conditions like epidermolysis bullosa.
Integrative Dermatology
Integrative dermatology combines traditional skin care with alternative methods. It focuses on treating the whole person, not just skin symptoms. This approach aims to find the root cause of skin issues.
Holistic Skin Care and Alternative Methods
Integrative dermatology uses both conventional and complementary treatments. Doctors may suggest dietary changes to improve skin health. They might recommend certain foods or supplements.
Natural remedies play a big role. Herbs and plant-based products can help many skin conditions. Aloe vera soothes burns and rashes. Tea tree oil fights acne.
Stress reduction is key. Techniques like meditation can calm the mind and skin. Yoga and deep breathing exercises may help some skin problems.
Sun protection is crucial. Integrative dermatologists stress the importance of sunscreen. They also teach about protective clothing and avoiding peak sun hours.
Some practices use the latest technologies alongside natural methods. LED light therapy can reduce inflammation. Lasers may treat scars or remove unwanted hair.
Home care is an important part of treatment. Patients learn to make natural face masks and scrubs. They get tips on gentle cleansing and moisturizing routines.
Personalized care plans are common. These consider a patient’s lifestyle, diet, and skin type. The goal is long-term skin health, not just quick fixes.
Accessing Dermatologic Care

Getting dermatology care involves scheduling appointments and understanding insurance options. These steps help patients receive timely and affordable skin treatments.
Scheduling an Appointment
Patients can book dermatology visits in several ways. Many clinics offer online patient portals for easy scheduling. Phone calls remain a common method to set up appointments.
Some dermatology offices use waitlists for faster access. Patients may get calls about last-minute openings. This helps fill gaps in the schedule.
Telehealth options have grown in recent years. Virtual visits allow quick consultations for minor skin issues. They can also help determine if an in-person exam is needed.
Urgent skin problems may get priority scheduling. Patients should describe their symptoms clearly when booking to ensure proper timing.
Insurance and PPO
Insurance coverage varies for dermatology services. Many plans require referrals from primary care doctors. Patients should check their policy details before scheduling.
PPO plans often offer more flexibility in choosing specialists. They may have a wider network of dermatologists to choose from. However, PPOs can have higher out-of-pocket costs.
Some dermatology treatments are considered cosmetic. These may not be covered by insurance. Patients should ask about costs upfront for such procedures.
Free or low-cost clinics provide dermatology care to uninsured patients. These services can be vital for those without regular insurance coverage.
Patients should always verify insurance acceptance with the dermatology office. This helps avoid unexpected bills after treatment.
Dermatology Specializations
Dermatology offers various areas of expertise for doctors to focus on. These specializations require extra training and skills to provide specific care for patients with different skin conditions.
Dermatopathology Insights
Dermatopathology combines dermatology and pathology. It focuses on studying skin samples under a microscope to diagnose diseases. Dermatopathologists examine skin biopsies to identify skin cancers, infections, and other disorders.
This field requires a keen eye for detail and deep knowledge of skin cell structures. Dermatopathologists work closely with dermatologists to provide accurate diagnoses. Their expertise helps guide treatment plans for complex skin conditions.
Dermatologist Education and Certification
Becoming a board-certified dermatologist involves extensive education and training. After medical school, doctors complete a residency in dermatology. This takes about three years.
During residency, they learn about skin diseases, treatments, and procedures. They gain hands-on experience with patients under supervision. After residency, many dermatologists pursue further specialization through fellowships.
To become board-certified, dermatologists must pass rigorous exams. These tests cover medical knowledge and patient care skills. Certification shows a doctor’s expertise in diagnosing and treating skin conditions.
Patient Resources and Support
Dermatology patients can access various resources and support systems to help them manage skin conditions. These include educational materials, online communities, and public health initiatives aimed at improving skin health.
Public Health and Dermatologic Education
Many cancer centers and hospitals offer support groups for patients and families dealing with skin conditions. These groups provide a space to share experiences and learn from others.
Public health campaigns raise awareness about skin diseases and promote prevention strategies. They often focus on sun protection and early detection of skin cancer.
Dermatology clinics may offer patient education programs. These teach people about their skin conditions and proper care techniques.
Some dermatologists partner with schools to educate children about skin health. This helps create good habits from an early age.
Online Resources and Community Support
The internet provides many ways for dermatology patients to find information and connect with others. Patient advocate resources offer support and education for those with skin diseases.
Online forums let patients discuss their experiences and share tips. These communities can be a source of emotional support.
Many dermatology practices have websites with helpful info. For example, some offer patient portals to access test results and communicate with doctors.
Reputable health websites provide articles on skin conditions. These can help patients understand their diagnoses and treatment options.
Smartphone apps exist for tracking symptoms and medication. They can help patients manage their skin care routines more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Dermatology services cover a wide range of skin, hair, and nail conditions. Patients often have questions about treatments, appointments, and finding the right doctor.
What conditions are typically treated by a dermatologist?
Dermatologists treat many skin issues. These include acne, eczema, psoriasis, and skin cancer. They also handle hair loss, nail problems, and cosmetic concerns.
Rashes, moles, and warts fall under their expertise too. Dermatologists can diagnose and treat over 3,000 skin conditions.
What is the distinction between general and medical dermatology?
General dermatology focuses on common skin issues. This includes acne treatment and routine skin checks.
Medical dermatology deals with more complex conditions. It covers diseases like psoriasis and skin cancer. Medical dermatologists may use advanced treatments and procedures.
How can I schedule an appointment with a dermatologist?
Most clinics offer phone and online booking options. You can call the office directly or use their website to set up a visit.
Some practices have patient portals for easy scheduling. You might need a referral from your primary care doctor, depending on your insurance.
What should I expect during my first visit to a dermatologist?
Your first visit will include a thorough skin exam. The doctor will ask about your medical history and any skin concerns.
They may take photos or samples if needed. The dermatologist will then discuss treatment options and answer your questions.
How do I find a reputable dermatologist in my area?
Start by asking your primary care doctor for recommendations. You can also check with your insurance provider for in-network options.
Online reviews and board certifications can help you find qualified dermatologists. The American Academy of Dermatology website has a “Find a Dermatologist” tool.
How do I access a dermatology patient portal?
Many dermatology practices offer online patient portals. These let you view test results, request appointments, and message your doctor.
To access the portal, ask your dermatologist’s office for instructions. They will provide login details and help you set up your account.